
Modal Analysis of a Water Pump Housing
A study and comparison of the vibration modes of a water pump housing tested using analog equipment and simulated in Siemens Femap software.
Group Project: 3 people
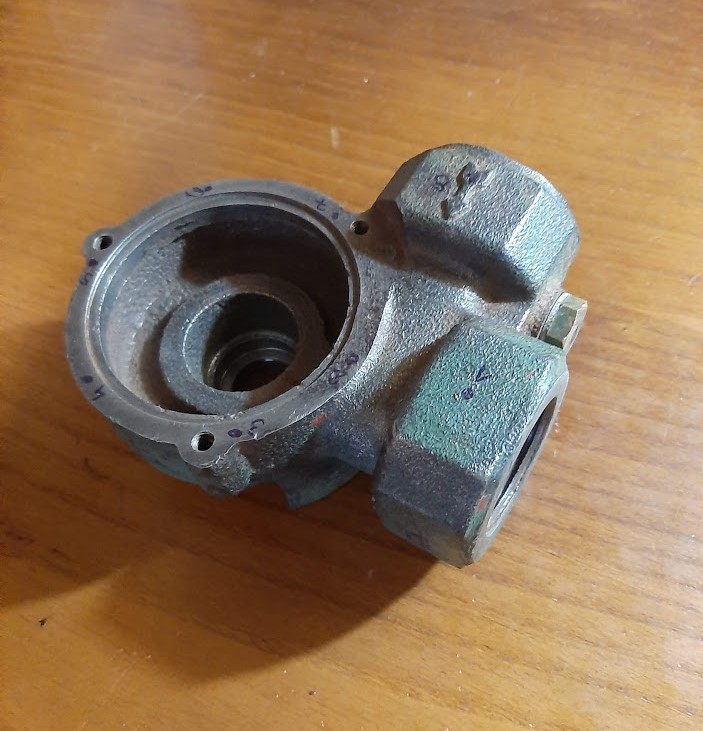
The object consists of a water pump housing produced from steel casting. The object's geometry was replicated virtually using 3D CAD software (Solidworks). Geometry was adjusted, eliminating unnecessary elements such as threads, fillets and some small defects that resulted from the casting process.

The part was uploaded to Siemens Femapap and meshing was performed. Upon analysing the geometry of the part, chosen type of finite element was solid parabolic, with tetahedral shape and 10 nodes. Small geometrical rework and mesh optimisation was performed to prevent unnecessary mesh failures. Finally, using the NX Nastran solver, Siemens Femap would return data for 12 main vibration modes and exaggerated maximum deformation could be observed.
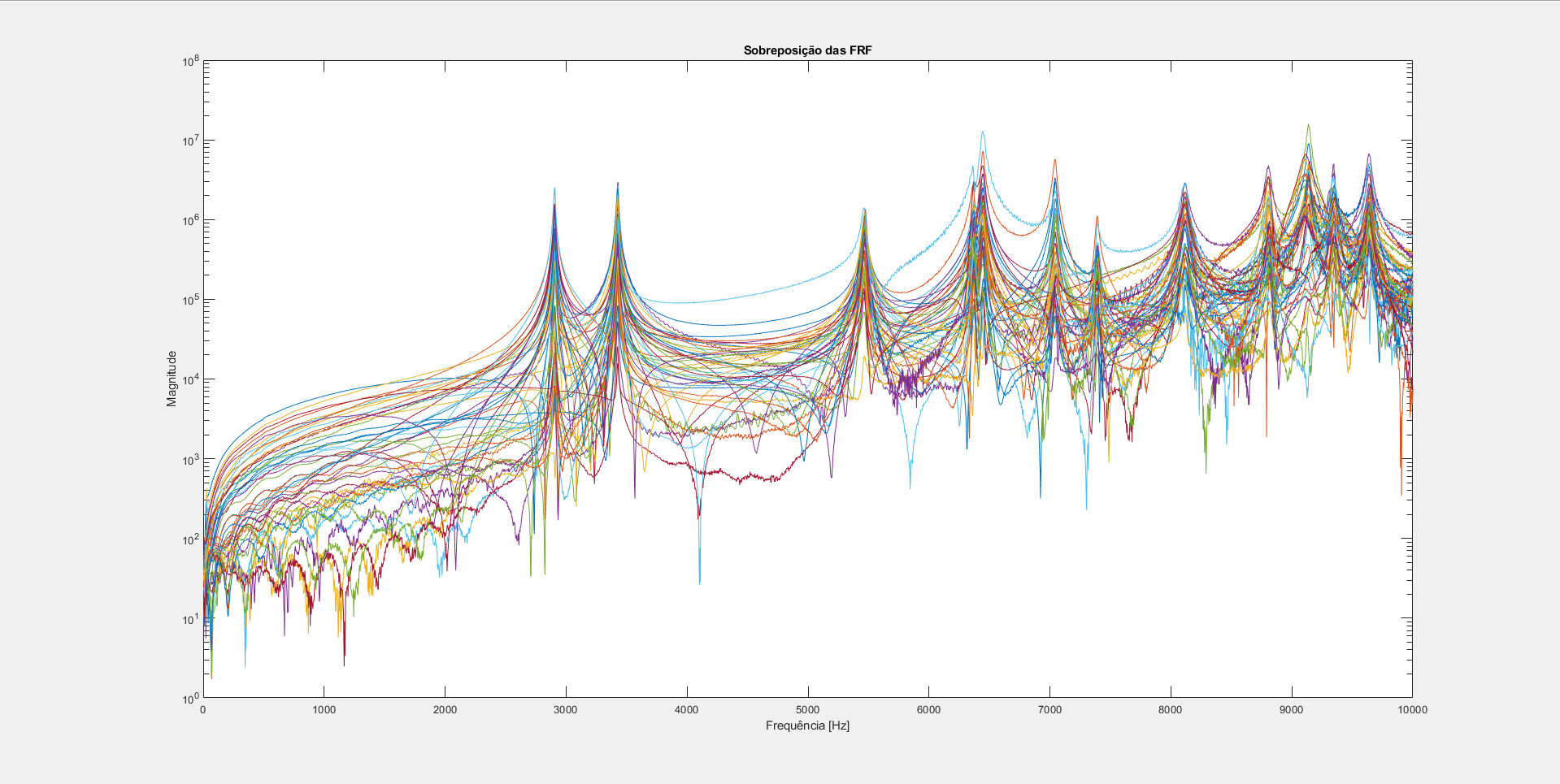
Using an impact hammer and accelerometers connected to a spectral analyzer, data was gathered to process and analyse on MATLAB. Sixteen different points were selected on the object for three different accelerometer positions (X, Y and Z). Uploading the analog data onto MATLAB, several diagrams were generated featuring:
This gallery features a compilation of pictures regarding the project. It includes pictures with the object and procedures, Siemens Femap showing the part, mesh and vibration modes and some of the diagrams that were extracted from MATLAB's output script.


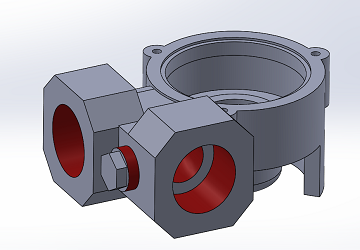
Designed using Solidworks. Areas marked as red were simplified (threads & small defects) in order to be properly imported to Siemens Femap.
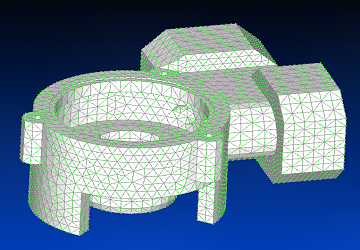
3D CAD Model imported and meshed in Siemens Femap (top view).
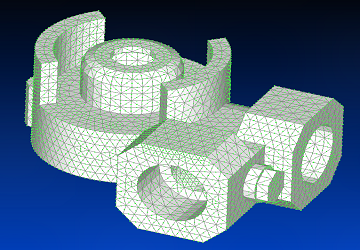
3D CAD Model imported and meshed in Siemens Femap (bottom view).
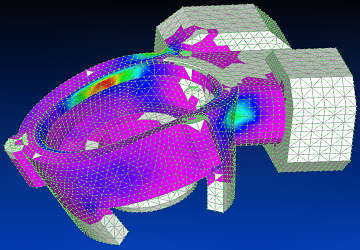
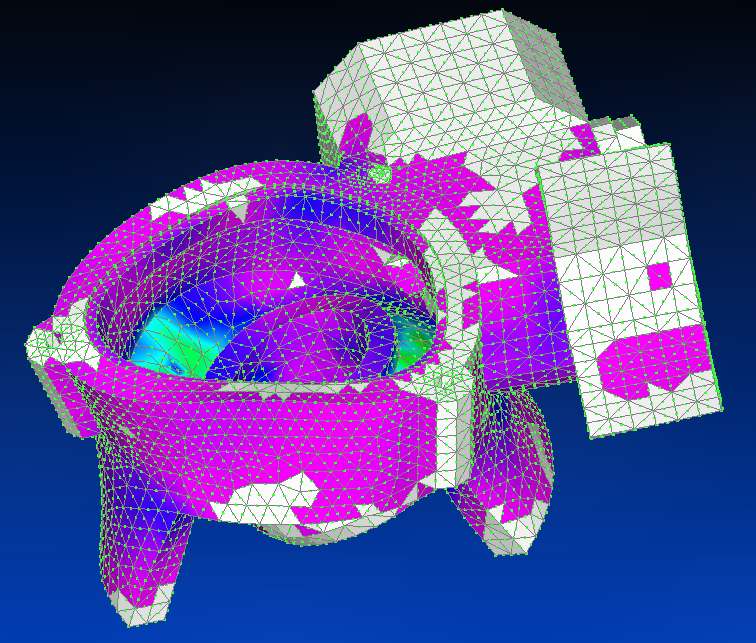
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the first vibration mode is shown (the remaining modes are shown at the end of the gallery).
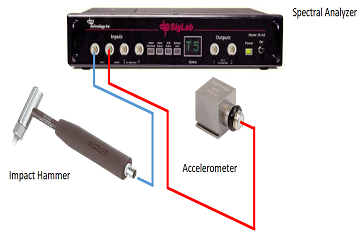
Using the hammer, accelerometers and a spectral analyzer, several data was acquired.
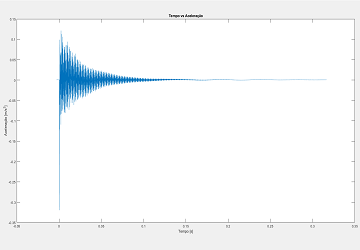
Computed from Y direction data points using MATLAB.
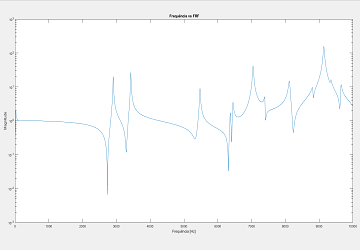
Computed from Y direction data points using MATLAB.
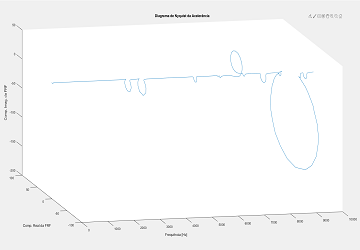
Computed from Y direction data points using MATLAB.
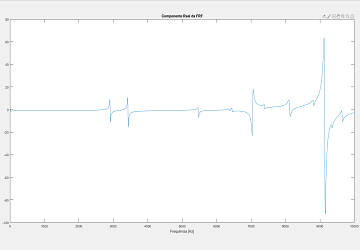
Computed from Y direction data points using MATLAB.
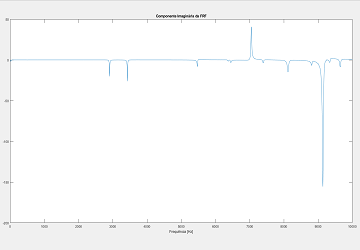
Computed from Y direction data points using MATLAB.
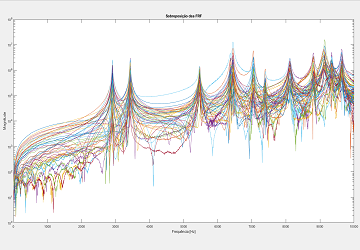
Computed from all data points using MATLAB.
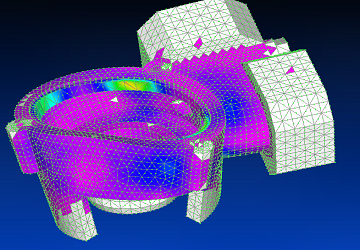
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the second vibration mode is shown.
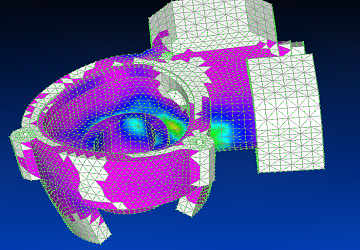
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the third vibration mode is shown.
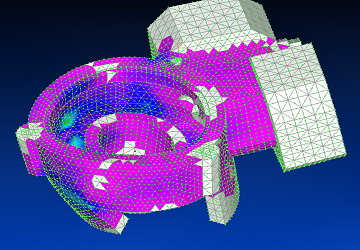
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the fourth vibration mode is shown.
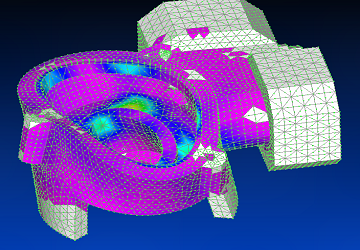
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the fifth vibration mode is shown.
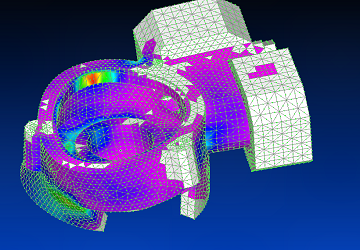
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the sixth vibration mode is shown.
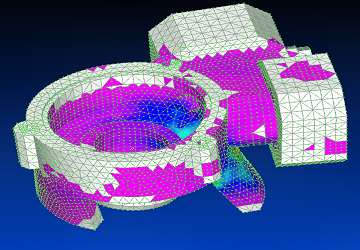
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the seventh vibration mode is shown.
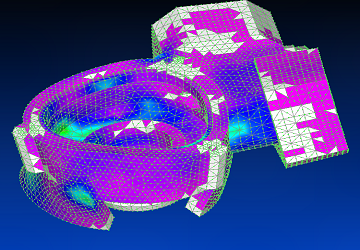
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the eighth vibration mode is shown.
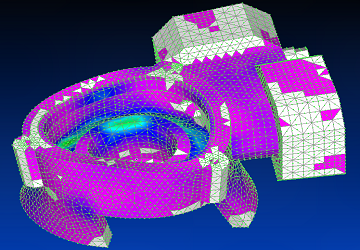
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the ninth vibration mode is shown.
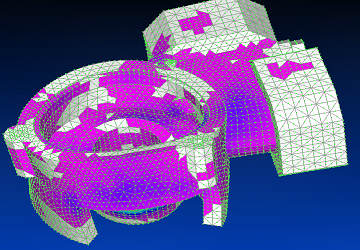
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the tenth vibration mode is shown.
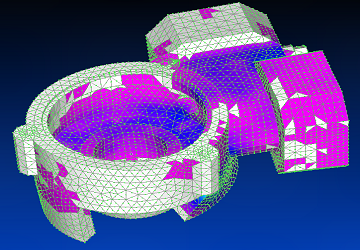
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the eleventh vibration mode is shown.
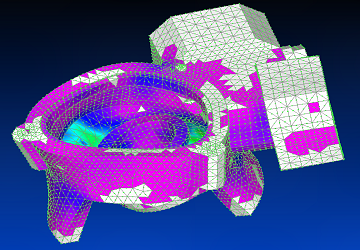
Using Siemens Femap with NX Nastran solver, the twelfth vibration mode is shown.
Perfoming a research experimental study using analog equipment to generate data from an object and then process it through a MATLAB script was a very complex and thorough process. It involved using knowledge from previous subjects to understand how the recorded data has to be processed. Using Siemens Femap to perform a modal analysis and comparing the results obtained from the experimental analysis proved that this software is a very valuable tool in modal analysis, and that this study is very important for every structural project.
Finite Element Analysis; CAE
Process experimental analog data through MATLAB scripts to create plots, charts and data reports.
Scripts and Algorithms